- +34 93 013 08 83
- sale@medicalnanorobots.com
- Autovia de Castelldefels C-31
- Km 190-5 (near Airport)
08820 El Prat de Llobregat (Barcelona)
The Future of Surgery Exploring the Rise and Impact of Surgical Robots in Modern Healthcare
The emergence of surgical robots marks a pivotal shift in modern healthcare, transforming traditional surgical methods and enhancing patient outcomes. According to a report from the American College of Surgeons, the global surgical robots market was valued at approximately $4.4 billion in 2020, with projections suggesting it will exceed $12.9 billion by 2027. This rapid growth is driven by advancements in robotic technology, which allows for minimally invasive procedures, reduced recovery times, and improved precision. Surgical robots, equipped with cutting-edge imaging and real-time data analysis capabilities, enable surgeons to perform complex operations with greater accuracy and control. As we explore the rise and impact of these advanced technologies, it is essential to understand their implications for surgical practices and patient care, as well as the challenges that accompany their integration into healthcare systems.
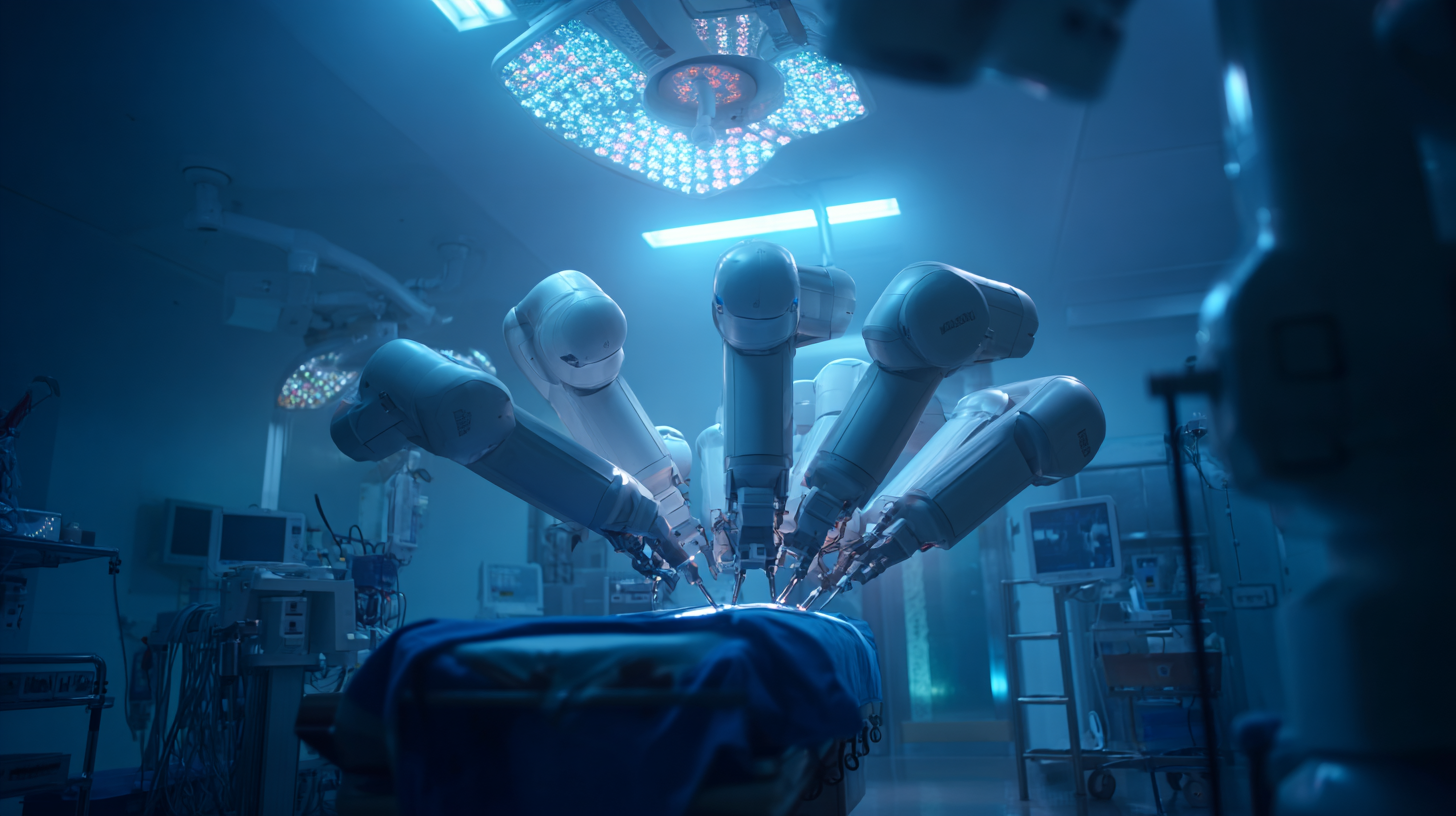
Understanding the Basics of Surgical Robotics and Their Functionality
Surgical robotics represents a transformative advancement in modern healthcare, offering precision and enhanced capabilities that traditional methods cannot match. At the core of surgical robotics lies a sophisticated system that combines high-definition 3D visualization with dexterous robotic arms manipulated by skilled surgeons. These robots are designed to perform minimally invasive procedures, which not only reduces patient recovery time but also minimizes scarring and complications. Such technology allows surgeons to operate with an elevated level of accuracy, enabling them to execute complex procedures with confidence.
Understanding the functionality of surgical robots is essential to appreciating their impact on healthcare. Typically, these systems consist of a console where the surgeon sits, equipped with controls that translate the surgeon's hand movements into precise actions executed by robotic instruments within the patient's body. Sensors and advanced software provide real-time feedback, enhancing the surgeon's control. As robotic systems continue to evolve, their integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning is anticipated to further augment their capabilities, paving the way for even more sophisticated surgical interventions in the future.
The Future of Surgery: The Impact of Surgical Robots in Modern Healthcare
This chart illustrates the growing prevalence of surgical robots in healthcare over the past five years, indicating a significant increase in their installation and utilization, reflecting advancements in surgical technology and a shift towards robotic-assisted procedures.
Identifying Key Advantages of Robotic Surgery Over Traditional Techniques
 Robotic surgery has emerged as a game-changing advancement in modern healthcare, providing numerous advantages over traditional surgical techniques. One of the primary benefits is the enhanced precision of robotic systems. Surgeons can perform delicate procedures with greater accuracy, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery also facilitates smaller incisions, which can lead to decreased scarring, less pain, and faster recovery times for patients.
Robotic surgery has emerged as a game-changing advancement in modern healthcare, providing numerous advantages over traditional surgical techniques. One of the primary benefits is the enhanced precision of robotic systems. Surgeons can perform delicate procedures with greater accuracy, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery also facilitates smaller incisions, which can lead to decreased scarring, less pain, and faster recovery times for patients.
Tips: When considering robotic surgery, patients should discuss with their healthcare providers about the specific benefits and risks associated with their condition. Understanding the technology behind robotic systems can help them make informed decisions about their treatment options.
In addition to precision, robotic surgery offers improved dexterity and flexibility. Robotic arms can navigate hard-to-reach areas of the body more easily than traditional tools, enabling surgeons to tackle complex procedures that might have been too challenging before. Furthermore, the incorporation of 3D visualization technology allows surgeons to see the surgical site in enhanced detail, which can contribute to better decision-making during operations.
Tips: It's essential to ensure that the surgical team is well-trained in robotic techniques and that the healthcare facility has experience with the specific robotic systems being used. Patients are encouraged to inquire about the surgeon’s experience with robotic-assisted procedures to further enhance their confidence in the chosen approach.
Assessing the Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Surgical Robots
The integration of surgical robots in modern healthcare has ushered in a new era of precision and efficiency. However, the implementation of these advanced technologies is not without challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the significant financial investment required for purchasing and maintaining robotic systems.
Hospitals must weigh the benefits of enhanced surgical outcomes against the high costs associated with training staff and maintaining the robotic platforms.
Additionally, the complexity of these systems can present a steep learning curve for surgeons. While robotic-assisted procedures can offer greater dexterity and visualization, mastering their use requires extensive training and practice. This may lead to a disparity in access to robotic surgery, particularly in smaller healthcare facilities that lack the resources to adopt such technologies. Moreover, regulatory hurdles and varying insurance coverage can further complicate the widespread adoption of surgical robots, making it critical for stakeholders to address these challenges to optimize the potential benefits of robotic surgery in patient care.
Exploring Future Innovations and Trends in Surgical Robotics Technology
The landscape of surgery is witnessing a transformative shift with the integration of advanced surgical robotics technology. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the surgical robotics market is expected to grow from USD 4.9 billion in 2021 to USD 12.6 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.5%. This surge is driven by the increasing demand for minimally invasive surgeries, which offer patients quicker recovery times and reduced postoperative complications.
Innovations in surgical robotics are not limited to enhanced dexterity and precision. The introduction of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is revolutionizing the field, enabling robots to assist in complex surgical procedures with greater accuracy. A study published in the Journal of Robotic Surgery highlights how AI-powered robotic systems can reduce surgical errors by up to 25%, thereby increasing patient safety. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to significantly enhance the capabilities of surgeons and the overall efficiency of healthcare systems, paving the way for more sophisticated approaches to patient care in the future.

Evaluating the Impact of Surgical Robots on Patient Outcomes and Recovery Times
The integration of surgical robots into modern healthcare has revolutionized patient outcomes and recovery times. Recent studies indicate that robot-assisted procedures enhance precision and significantly minimize invasiveness, leading to less postoperative pain and quicker recovery. For instance, robot-assisted stereotactic surgery has been shown to improve hematoma evacuation in cases of intracerebral hemorrhage compared to traditional frame-based methods, thus decreasing the likelihood of poor patient outcomes and promoting faster rehabilitation.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols have further transformed the surgical landscape by standardizing perioperative care, which aligns seamlessly with the capabilities of robotic surgery. Implementation of these protocols, although challenging, is evidenced to reduce surgical stress and foster quicker returns to functional health. Moreover, findings from intuitive studies corroborate that robotic surgical systems facilitate access to high-quality care, particularly in underserved areas, thereby widening the scope of effective treatment and improving overall patient safety. As technology evolves, integrating artificial intelligence and personalized care within surgical practices promises even greater enhancements in patient outcomes and recovery trajectories.
The Future of Surgery: Exploring the Rise and Impact of Surgical Robots in Modern Healthcare
| Surgical Procedure | Robotic System | Average Recovery Time (Days) | Patient Outcome Rating (1-10) | Complication Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostatectomy | Da Vinci Surgical System | 3 | 9 | 1.5 |
| Cholecystectomy | Versius Surgical System | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| Hysterectomy | Laparoscopic Robotic System | 5 | 7 | 3 |
| Cardiac Valve Repair | CorPath System | 7 | 8.5 | 1 |
| Spinal Surgery | Medtronic Stealth | 4 | 9.2 | 2.5 |
Related Posts
-

Transforming Healthcare: The Future of Robotic Surgical Systems in Minimally Invasive Procedures
-

Exploring the Future of Medicine with Robotic Surgical Systems in Minimally Invasive Procedures
-
Unlocking the Future of Healthcare: Innovations in New Surgical Techniques You Need to Know
-
Understanding the Role of a Surgery Surgeon in Modern Medical Practices
-
The Future of Healthcare Transforming Patient Outcomes with Robotic Surgery Innovations
-
Revolutionizing Surgery with the Latest Innovations in New Surgical Robots