- +34 93 013 08 83
- sale@medicalnanorobots.com
- Autovia de Castelldefels C-31
- Km 190-5 (near Airport)
08820 El Prat de Llobregat (Barcelona)
Top 10 Surgical Access Techniques for Improved Patient Outcomes
Surgical access plays a critical role in determining the success of surgical procedures and overall patient outcomes. As healthcare continues to evolve, advancements in surgical access techniques have shown promise in reducing complications, minimizing recovery times, and improving patient satisfaction. According to a report by the American College of Surgeons, approximately 25% of complications in surgery can be attributed to inadequate surgical access, highlighting the importance of refining these techniques.
Dr. Emily Tran, a leading expert in surgical access and author of numerous studies on the subject, emphasizes, "Effective surgical access is not just about reach; it's about achieving the best possible outcomes for our patients." With the integration of minimally invasive approaches and innovative technologies, the landscape of surgical access is rapidly changing. Surgeons who adopt these techniques can significantly enhance their operational efficiency, subsequently leading to better recovery trajectories.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 surgical access techniques that are reshaping the field, focusing on their effectiveness, safety profiles, and the potential for improved patient experiences. Understanding and implementing these strategies is crucial for modern surgical practice as we strive to provide the highest standard of care.
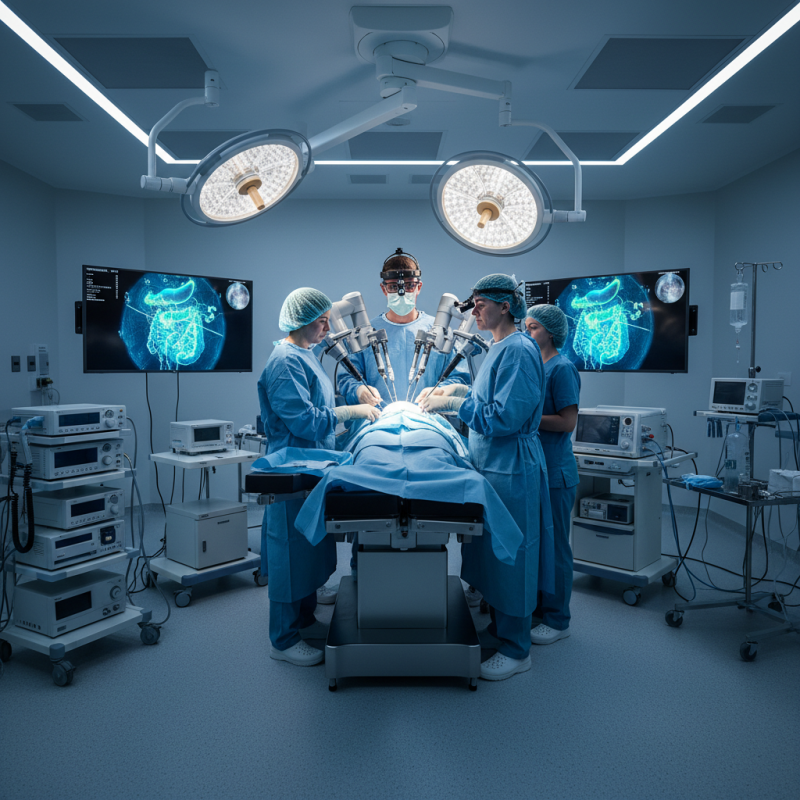
Overview of Surgical Access Techniques and Their Importance
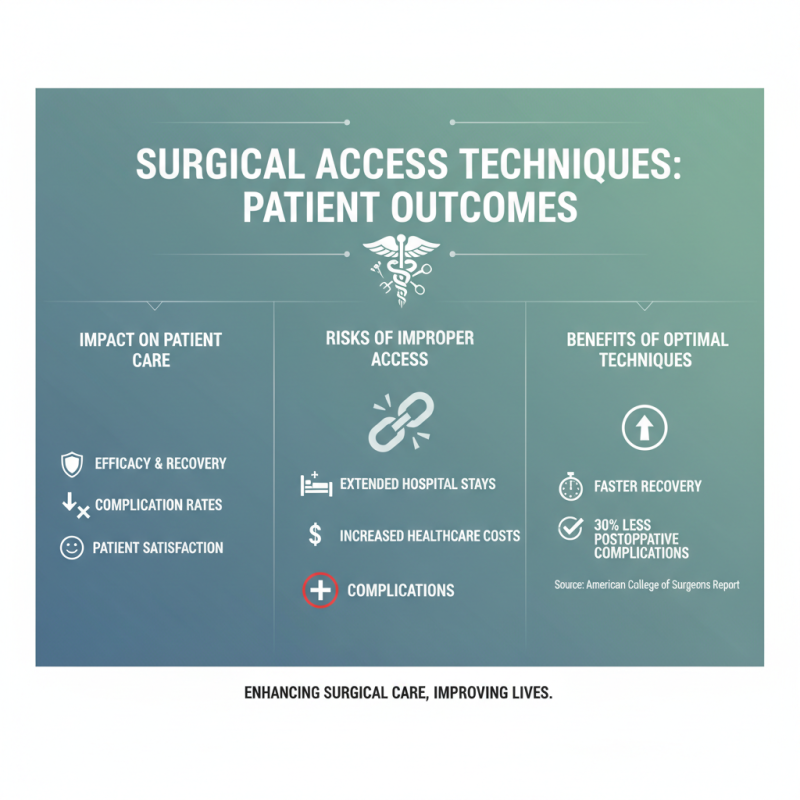
Surgical access techniques play a critical role in determining patient outcomes during surgical procedures. These techniques not only influence the efficacy of the surgery but also directly affect recovery times, complication rates, and overall patient satisfaction. According to a report by the American College of Surgeons, complications can arise from improper access, leading to extended hospital stays and increased healthcare costs. For instance, studies show that enhanced recovery protocols are associated with a 30% reduction in postoperative complications when optimal access techniques are employed.
Moreover, the choice of surgical access technique can significantly impact surgical precision and the ability to perform minimally invasive procedures, which have gained momentum in recent years. A survey from the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons indicates that procedures utilizing laparoscopic access have been associated with a 40% reduction in postoperative pain and faster recovery times compared to traditional open techniques. By integrating advanced surgical access methodologies, healthcare providers can not only improve clinical outcomes but also enhance the overall patient experience, ultimately contributing to higher rates of recovery and lower incidence of surgical morbidity.
Minimally Invasive Surgery: Techniques and Benefits for Patients
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionized the field of surgical techniques, offering numerous benefits for patients, including reduced recovery times and decreased postoperative pain. According to a 2022 report from the American College of Surgeons, patients undergoing MIS typically experience a reduction in hospital stay by 30-50% compared to traditional open surgery. This not only enhances patient comfort but also significantly lowers healthcare costs, with potential savings exceeding $20,000 per patient when factoring in reduced readmission rates and shorter rehabilitation periods.
The adoption of advanced surgical access techniques is crucial in maximizing these benefits. Techniques such as laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery have been associated with lower complication rates and improved surgical precision. A comprehensive review published in the Journal of Surgical Research highlights that MIS approaches can result in 23% fewer complications overall, emphasizing the importance of training and implementation of these techniques in surgical practice. By prioritizing minimally invasive methods, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes, leading to safer surgeries and greater satisfaction rates among patients post-procedure.
Top 10 Surgical Access Techniques for Improved Patient Outcomes
This chart illustrates the percentage of improvement in patient outcomes associated with various surgical access techniques. Techniques such as laparoscopy and robotic surgery show significant benefits, reflecting advancements in minimally invasive surgery.
Traditional Surgical Access Methods: Comparison and Use Cases
Traditional surgical access methods, such as open surgery, laparoscopy, and thoracotomy, continue to play a crucial role in surgical practice despite the rise of minimally invasive techniques. Open surgery allows for direct visualization and access to internal structures, which can be vital in complex cases.
According to a 2021 report from the American College of Surgeons, approximately 60% of major surgeries still employ traditional open approaches, particularly in cases involving significant anatomical alterations or extensive tissue removal. This method is often chosen due to its ability to provide comprehensive access and facilitate multifaceted procedures, which can be critical for patient safety and outcomes.
Laparoscopy, a less invasive alternative, offers benefits such as reduced postoperative pain and quicker recovery times. A study published in the Journal of Surgical Research indicated that patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery experienced a 30% shorter hospital stay compared to those who had open surgery. However, laparoscopic techniques may not be suitable for all patients or conditions, as they require specialized training and can be limited in cases involving obesity or extensive scarring.
In this context, thoracotomy remains an indispensable technique for thoracic surgeries, where direct access to thoracic organs is necessary. In summary, while the surgical landscape evolves with new technologies, understanding when to use traditional methods is essential for optimizing patient outcomes.
Emerging Technologies in Surgical Access: Innovations and Trends
Emerging technologies in surgical access are rapidly transforming the landscape of surgical procedures, leading to improved patient outcomes and enhanced operational efficiency. Innovations such as robotic-assisted surgeries and advanced imaging techniques are redefining how surgeons approach complex procedures. These technologies not only enable more precise incisions but also minimize patient recovery time, reducing the risk of complications.
One of the prominent trends in surgical access is the increasing adoption of minimally invasive techniques. By utilizing small incisions and sophisticated instruments, surgeons can perform operations with less trauma to the body. This approach has been shown to significantly decrease postoperative pain and accelerate healing. Hospitals are also investing in training for surgical teams to ensure that they are adept at using these new technologies, which ultimately contributes to better patient care.
Tips: When considering surgical options, patients should inquire about the availability of minimally invasive procedures and the specific technology being employed. Engaging in discussions about the surgeon’s experience with these advanced techniques can also provide reassurance and improve the decision-making process. Keeping abreast of the latest advancements in surgical technology is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Evaluating Patient Outcomes: Metrics for Success in Surgical Procedures
In the realm of surgical access techniques, the evaluation of patient outcomes has become a cornerstone for measuring the efficacy of procedures. Metrics such as complication rates, recovery times, and overall patient satisfaction are crucial for understanding the success of surgical interventions. By systematically collecting and analyzing these data points, healthcare providers can identify best practices that enhance patient care while minimizing risks associated with various surgical approaches.
Patient-reported outcomes, including pain levels and functional status post-surgery, also offer valuable insights. Incorporating these subjective measures alongside objective clinical data gives a comprehensive view of the patient journey. For instance, tracking rehabilitation progress and post-operative quality of life allows surgeons to refine their techniques and improve the patient experience. In this context, continuous feedback loops between surgical teams and patients not only foster trust but also facilitate innovation in surgical methodologies aimed at optimizing health outcomes.
Top 10 Surgical Access Techniques for Improved Patient Outcomes
| Technique | Success Rate (%) | Average Recovery Time (days) | Complication Rate (%) | Patient Satisfaction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laparoscopic Surgery | 92 | 7 | 4 | 89 |
| Robotic-assisted Surgery | 95 | 5 | 3 | 91 |
| Traditional Open Surgery | 87 | 10 | 9 | 75 |
| Endoscopic Surgery | 90 | 4 | 2 | 88 |
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | 89 | 6 | 5 | 85 |
| Percutaneous Surgery | 91 | 5 | 2 | 90 |
| Transcatheter Surgery | 93 | 8 | 4 | 87 |
| Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) | 88 | 7 | 6 | 84 |
| Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES) | 85 | 9 | 7 | 80 |
| Hybrid Techniques | 92 | 6 | 3 | 86 |
Related Posts
-
Exploring the Future of Healthcare: How Robotic Surgery Procedures Are Transforming Patient Outcomes
-
10 Essential Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of Robotic Surgery Robots in Healthcare
-

How to Prepare for Surgery at Home Tips and Best Practices
-
Revolutionizing Surgery with the Latest Innovations in New Surgical Robots
-

2025 Top Robotic Surgery Market Trends and Innovations You Need to Know
-

Best 10 Advantages of Hybrid Surgery For Modern Medical Practices