- +34 93 013 08 83
- sale@medicalnanorobots.com
- Autovia de Castelldefels C-31
- Km 190-5 (near Airport)
08820 El Prat de Llobregat (Barcelona)
What is Robotic Surgical Systems and How Do They Transform Healthcare
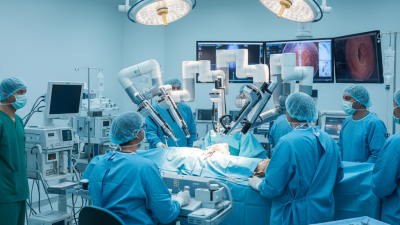
Robotic Surgical Systems have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in the healthcare sector, fundamentally changing the landscape of surgical procedures. These systems, which integrate advanced robotics with minimally invasive techniques, enhance precision and control for surgeons, leading to better patient outcomes. Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in the field of robotic surgery, states, "The advent of rob surgical systems allows us to perform complex surgeries with precision that was unimaginable just a decade ago." This highlights the transformative potential of these technologies in delivering superior surgical care.
The integration of rob surgical systems into clinical practice not only improves surgical accuracy but also reduces recovery times and minimizes complications. Surgeons can perform intricate maneuvers through small incisions, which lessens trauma to the body and promotes faster healing. As the healthcare industry continues to embrace robotic technologies, the implications for patient care and surgical practice become increasingly profound. With innovations expanding rapidly, ongoing research and development in rob surgical systems promise to usher in a new era of surgery, one where enhanced capabilities lead to improved patient experiences and outcomes.
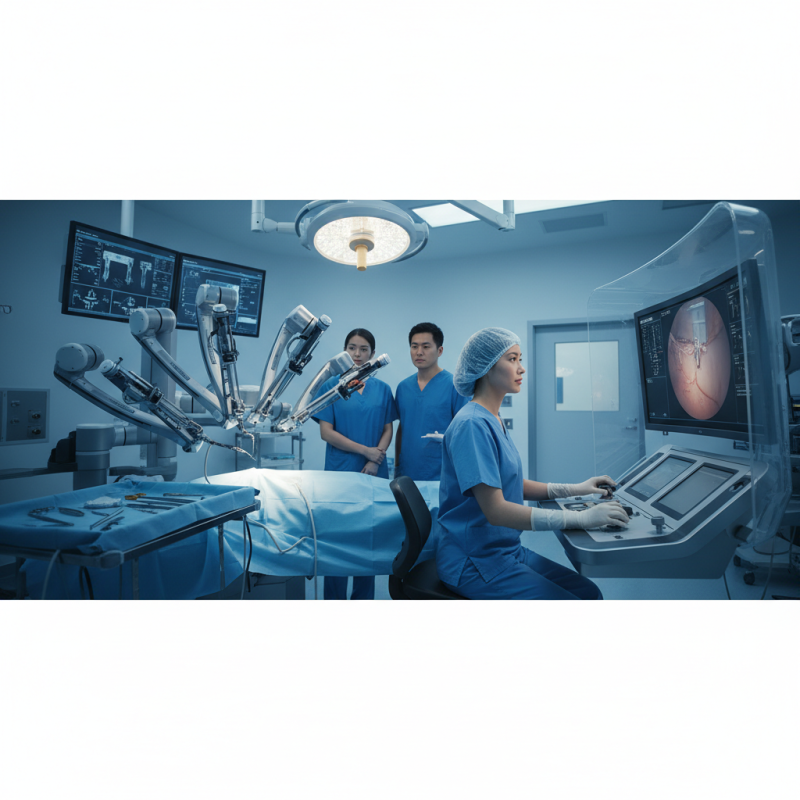
Definition of Robotic Surgical Systems and Their Key Features
Robotic Surgical Systems represent a revolutionary advancement in the field of healthcare, specifically in surgical procedures. Defined as computer-assisted systems that enhance the capabilities of surgeons, these systems incorporate precision instruments, advanced imaging, and intuitive control interfaces. One of the key features of robotic surgical systems is their ability to perform minimally invasive surgeries, resulting in smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and quicker recovery times for patients. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global robotic surgical systems market was valued at approximately $4.4 billion in 2020, illustrating their growing adoption in healthcare settings.
The integration of robotics in surgery also enhances procedural accuracy and surgeon efficiency. Features such as 3D visualization and fine motor control allow surgeons to perform complex tasks with enhanced dexterity, reducing the risks associated with traditional open surgery. A study published in the journal Surgical Endoscopy noted that robotic-assisted surgeries resulted in a 20% decrease in postoperative complications compared to conventional methods. Furthermore, the projected growth rate of the robotic surgical systems market is estimated to reach 18.2% from 2021 to 2028, which underscores the increasing reliance on these technologies to refine surgical practices and improve patient outcomes.
Historical Development of Robotic Surgical Systems in Medicine
The historical development of robotic surgical systems in medicine traces back to the late 20th century, illustrating a significant evolution in surgical practices. Initially, the concept of using robotic technology in surgery emerged from the desire to enhance precision and reduce the invasiveness of traditional procedures. Early prototypes, primarily designed for exploratory tasks, laid the groundwork for more sophisticated systems. Eventually, the integration of advanced imaging techniques and computer technology allowed for a greater degree of control and accuracy in surgical operations.
As the technology advanced, pivotal milestones marked the progression of robotic surgery. In the early stages, systems utilized primarily for remote surgeries demonstrated the potential to operate on patients in different geographical locations. This novel approach not only expanded access to expert care but also set the stage for developments in minimally invasive procedures. Over the years, the refinement of robotic systems enabled surgeons to perform complex surgeries with improved dexterity and visualization, transforming the landscape of surgical medicine and leading to better patient outcomes and recovery times.
The continued evolution of robotic surgical systems is characterized by ongoing research and development aimed at enhancing their capabilities. By incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning, modern systems are being designed to assist surgeons in real-time, making procedures safer and more efficient. This ongoing transformation reflects a broader trend in healthcare, where technology increasingly plays a crucial role in shaping patient care and treatment methodologies.
Historical Development of Robotic Surgical Systems in Medicine
Benefits of Robotic Surgery for Patients and Healthcare Providers
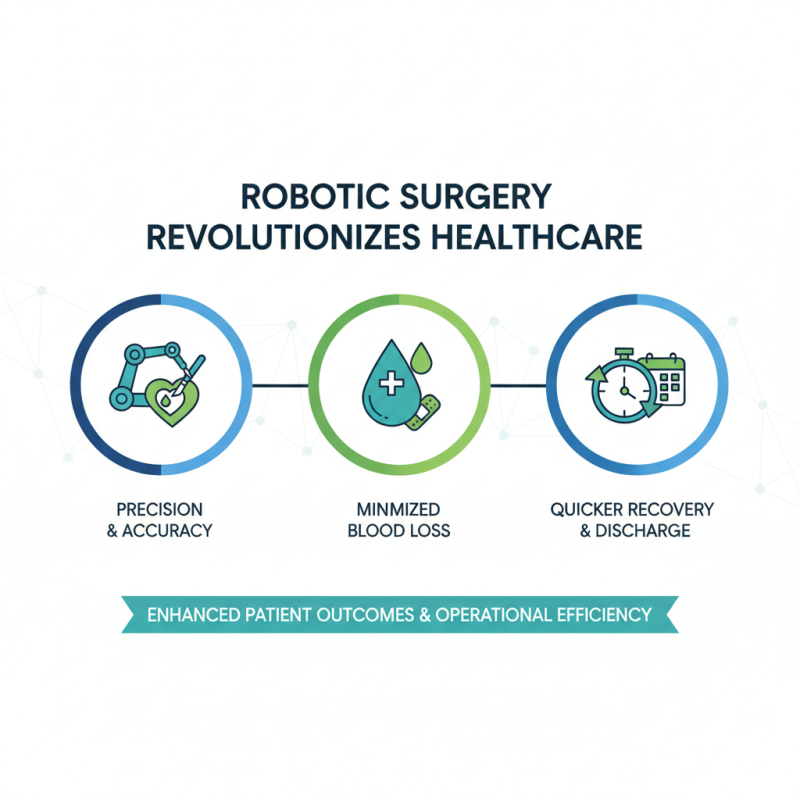
Robotic surgery is revolutionizing the way healthcare providers approach surgical procedures, offering a myriad of benefits that enhance patient outcomes and operational efficiency. One significant advantage is the precision that robotic systems deliver. Surgeons can perform intricate movements with greater accuracy, reducing the risk of complications and minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This precision leads to less blood loss during surgery, which contributes to a quicker recovery time and reduced hospital stays for patients.
Additionally, robotic surgical systems enhance the overall patient experience. Minimally invasive techniques often result in smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain and scarring. As a result, patients can return to their daily activities faster, experiencing shorter recovery periods. For healthcare providers, robotic surgery can also streamline surgical workflows, allowing for more procedures to be performed in a shorter timeframe. This improved efficiency can lead to better utilization of resources and enhanced patient care, ultimately transforming the landscape of surgical medicine and patient management.
Challenges and Limitations of Robotic Surgical Systems Implementation
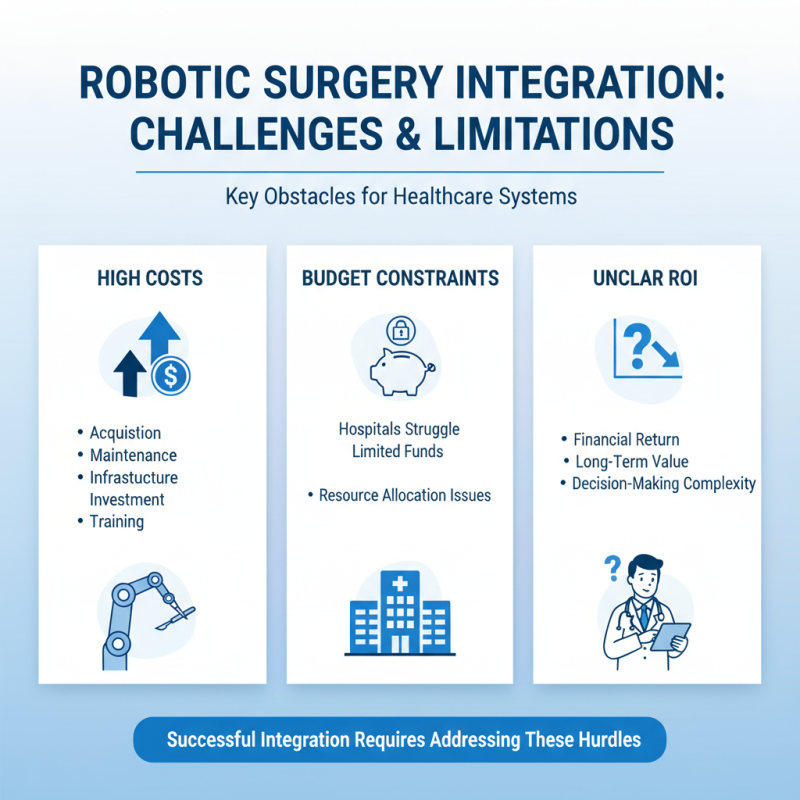
The implementation of robotic surgical systems in healthcare presents significant challenges and limitations that must be addressed for successful integration. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost associated with the acquisition, maintenance, and operation of these advanced technologies. Hospitals often face budget constraints, which can make it difficult to invest in the necessary infrastructure and training required for optimal use of robotic systems. Additionally, the financial return on investment may not be immediately clear, further complicating the decision-making process for healthcare institutions.
Another significant challenge lies in the training and proficiency of surgical staff. Although robotic systems can enhance precision and control during procedures, they require surgeons to possess specialized skills and familiarity with the technology. This necessitates extensive training programs, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Furthermore, the learning curve for new users can result in initial complications during surgeries, potentially affecting patient outcomes. Ensuring that surgical teams are adequately prepared to utilize these systems is crucial, yet it poses a logistical challenge for healthcare facilities.
Lastly, there are concerns regarding the variability in adoption across different medical centers. While larger hospitals may have the resources to embrace robotic surgery, smaller facilities may struggle due to limited budgets and staffing. This disparity can lead to unequal access to cutting-edge surgical techniques, ultimately affecting patient care and outcomes within various communities. Addressing these limitations is essential for improving the overall success and integration of robotic surgical systems in modern healthcare.
Future Trends and Innovations in Robotic Surgery Technology
The advancement of robotic surgical systems is poised to revolutionize healthcare by introducing innovative technologies that enhance precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Future trends indicate a shift towards more autonomous surgical robots, which will utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to assist surgeons in complex procedures. These systems will not only analyze patient data in real-time but also learn from each surgery, continuously improving their capabilities and decision-making processes.
Moreover, the integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) into robotic surgery is set to transform surgical training and pre-operative planning. Surgeons will be able to visualize 3D models of patient anatomy, interacting with them in real-time to strategize surgical approaches. This immersive technology can enhance skill acquisition for trainees and provide experienced surgeons with new perspectives on challenging cases, ultimately leading to better surgical precision and reduced recovery times for patients. As these innovations evolve, the landscape of surgical procedures will become more efficient, safer, and tailored to individual patient needs.
What is Robotic Surgical Systems and How Do They Transform Healthcare
| Dimension | Current Trends | Future Innovations | Impact on Healthcare |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | Increased use of robotic platforms for precise incisions and reduced recovery times. | Integration of AI for enhanced decision-making support during surgeries. | Improved patient outcomes and shorter hospital stays. |
| Training and Simulation | Virtual reality simulations for training surgeons. | Augmented reality applications for real-time guidance during surgery. | Enhanced surgeon proficiency leading to better patient trust and safety. |
| Robotic Assistance | Use of robotic systems in a variety of surgical disciplines. | Development of softer, more flexible robotic arms for intricate procedures. | Wider applicability in remote areas, potentially reducing access disparities. |
| Data Integration | Incorporation of health data analytics to improve surgical planning. | AI-driven predictive analytics for surgical outcomes. | More personalized patient care tailored to individual needs. |
Related Posts
-

2025 How to Effectively Use Robotic Surgery for Enhanced Patient Outcomes
-
Top Robotic Surgical Systems Trends Innovations and Future Prospects for 2025
-
How to Choose the Best Surgical Robots for Your Hospital Needs
-
The Future of Healthcare Transforming Patient Outcomes with Robotic Surgery Innovations
-

Transforming Healthcare: The Future of Robotic Surgical Systems in Minimally Invasive Procedures
-

Exploring the Future of Medicine with Robotic Surgical Systems in Minimally Invasive Procedures