- +34 93 013 08 83
- sale@medicalnanorobots.com
- Autovia de Castelldefels C-31
- Km 190-5 (near Airport)
08820 El Prat de Llobregat (Barcelona)
Why Robotic Surgery is Revolutionizing Modern Medicine?
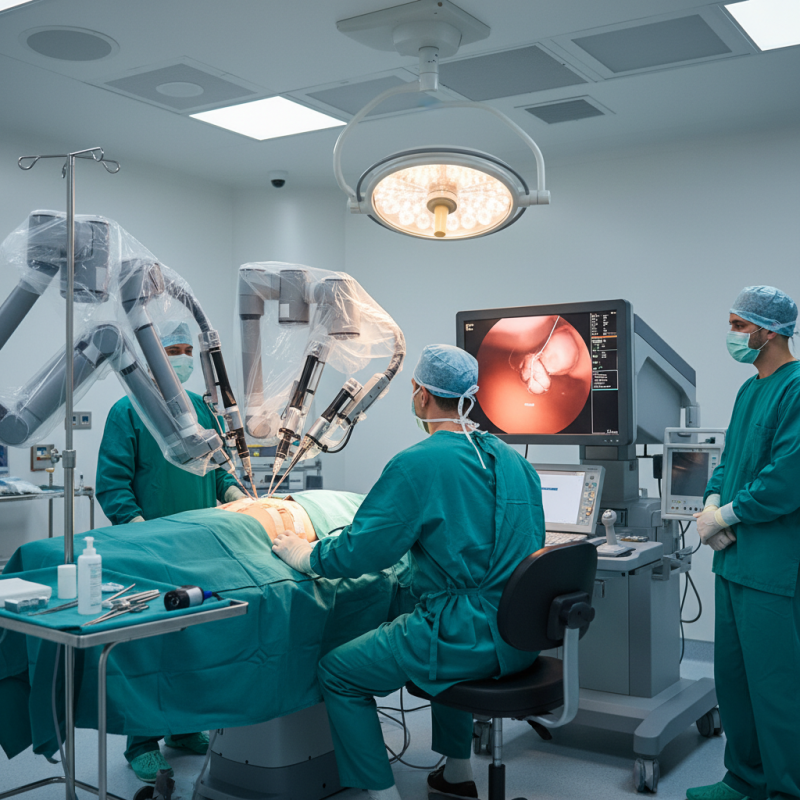
Robotic surgery is transforming the landscape of modern medicine. This innovative approach offers precision that traditional methods cannot match. Surgeons now use robotic systems to enhance their skills, making procedures safer and less invasive. With robotic assistance, patients experience smaller incisions and quicker recovery times.
However, this revolution comes with challenges. Access to robotic surgery remains limited in some regions. Not all hospitals have the resources for advanced robotic systems. Training medical professionals to use these systems effectively is also a concern.
Despite these obstacles, the potential benefits are undeniable. Enhanced visualization and dexterity can lead to better patient outcomes. Robotic surgery, while still evolving, promises a future where surgical risks are minimized. The journey ahead requires careful consideration and ongoing improvements.
The Evolution of Robotic Surgery in the Medical Field
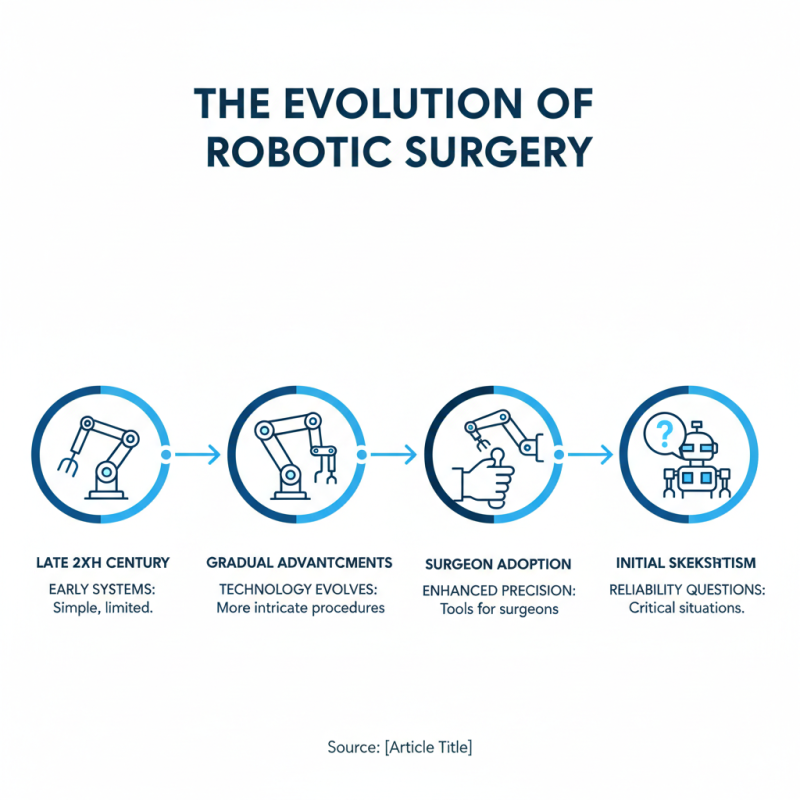
The journey of robotic surgery began in the late 20th century. Early systems were simple and limited in capability. Gradually, advancements in technology allowed for more intricate procedures. Surgeons started to embrace robots as tools to enhance precision. However, the initial skepticism was evident. Many questioned the reliability of machines in critical situations.
As the years passed, robotic systems evolved significantly. They became capable of minimally invasive techniques. This shift led to shorter recovery times for patients. Surgeons could perform delicate operations with enhanced visualization and control. Yet, challenges remain. Training medical professionals to use these systems effectively is critical. Some still struggle with the concept of a robot assisting in surgery.
Public perception is also an area that needs focus. Patients may hesitate to trust robots completely. Addressing these concerns requires ongoing education and transparency. While robotic surgery continues to change the landscape of medicine, it’s clear that room for improvement exists. Balancing technology with human expertise will remain vital for future advancements.
Key Advantages of Robotic Surgery over Traditional Techniques
Robotic surgery is changing modern medicine. It offers precision that traditional techniques often cannot match. For example, studies show that robotic-assisted surgeries can lead to fewer complications. A report from the American Urological Association states that these techniques can reduce hospital stays by up to 20%.
One key advantage is enhanced visualization. Surgeons can see the surgical site in 3D. This allows for more accurate movements. A higher degree of control can lower the risks of errors. However, training is crucial. Surgeons must be proficient in both technical skills and the robotic interface. Mistakes in setup or operation can occur.
Tips: Always choose surgeons familiar with robotic systems. Ask about their experience. Research shows surgical teams using these technologies often yield better outcomes. Yet, it is essential to discuss all options with your doctor. Each case is unique and may require different approaches.
Types of Robotic Surgical Systems and Their Applications
Robotic surgical systems are transforming the landscape of modern medicine. Various types cater to different surgical needs. One well-known type is the teleoperated surgical robot. Surgeons control robotic arms from a console. This offers precision and dexterity that human hands might struggle with. Such systems are often used in procedures like prostatectomies and hysterectomies.
Another type is the robotic endoscope. This device allows for minimally invasive procedures. It is used in gastrointestinal surgeries, providing a detailed view inside the body. The robotic endoscope enhances visualization, yet it presents challenges. Surgeons must adapt their skills to new technology. Familiarity is critical, and the learning curve can be steep.
Lastly, there are hybrid systems. These integrate robotic assistance with traditional methods. They can be beneficial in complex surgeries. However, they may require more training and adjustment. Surgeons must balance the advantages with these potential drawbacks. As this technology evolves, reflecting on these nuances remains essential for better patient care.
Robotic Surgery Applications and Their Growth in Modern Medicine
Challenges and Limitations of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery has indeed changed how we view medical procedures. However, it faces significant challenges and limitations that cannot be overlooked. One major concern is the high cost associated with these systems. Surgical robots may require extensive financial investment, which can limit accessibility for smaller hospitals. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and training costs can strain already tight budgets.
Another critical issue is the learning curve for surgeons. While robotic systems can enhance precision, mastering their use takes time and effort. Surgeons need extensive training to operate these machines effectively. Errors during the learning phase can lead to complications, impacting patient safety. Patients must trust their surgeons not just for their skills, but also for their familiarity with robotic technology.
Patient outcomes, though often improved, are not guaranteed. Complications can still arise, sometimes exacerbated by the robotic approach. Surgeons may get too reliant on technology and overlook traditional techniques. This dependency can create a disconnect during complex procedures. (Balancing robotic assistance with human expertise remains a constant challenge) in this evolving field.
Future Trends and Innovations in Robotic Surgery Technology
Robotic surgery is transforming healthcare. Innovations in robotic technology present exciting possibilities for the future. According to recent reports, the global surgical robotics market is projected to reach $20 billion by 2025. This surge points to growing adoption across various medical fields.
New technologies are enhancing precision. For instance, minimally invasive robots can perform complex procedures with greater accuracy. A study highlighted that robotic-assisted surgeries can reduce recovery time by 30%. However, these advancements bring challenges. Surgeons must adapt to new systems, which requires training and practice. Not all surgeries may benefit equally from robotic assistance.
Data analysis indicates a potential skill gap among medical teams. While robots can assist, human oversight remains crucial. There is a risk of over-reliance on technology. Furthermore, costs associated with robotic systems can be prohibitive. As such, equitable access remains a key concern. The path forward includes addressing these hurdles while continuing to leverage robotic technologies.
Related Posts
-
What is the Future of Robotic Surgery Market Trends and Opportunities
-
What is Robotic Surgery and How Does it Transform Modern Medicine
-
The Future of Healthcare Transforming Patient Outcomes with Robotic Surgery Innovations
-

2025 How to Effectively Use Robotic Surgery for Enhanced Patient Outcomes
-

2025 Top Robotic Surgery Market Trends and Innovations You Need to Know
-

Why the Robotic Surgery Market is Revolutionizing Healthcare Today